2.2.3 Trolley travelling mechanism
Kingda ladle crane (or casting crane) trolley travelling mechanism consists of motor, reducer, brake, transmission shaft, coupling, wheel group, etc., and can drive the trolley to move horizontally. The travelling mechanism has 4 arrangement forms:
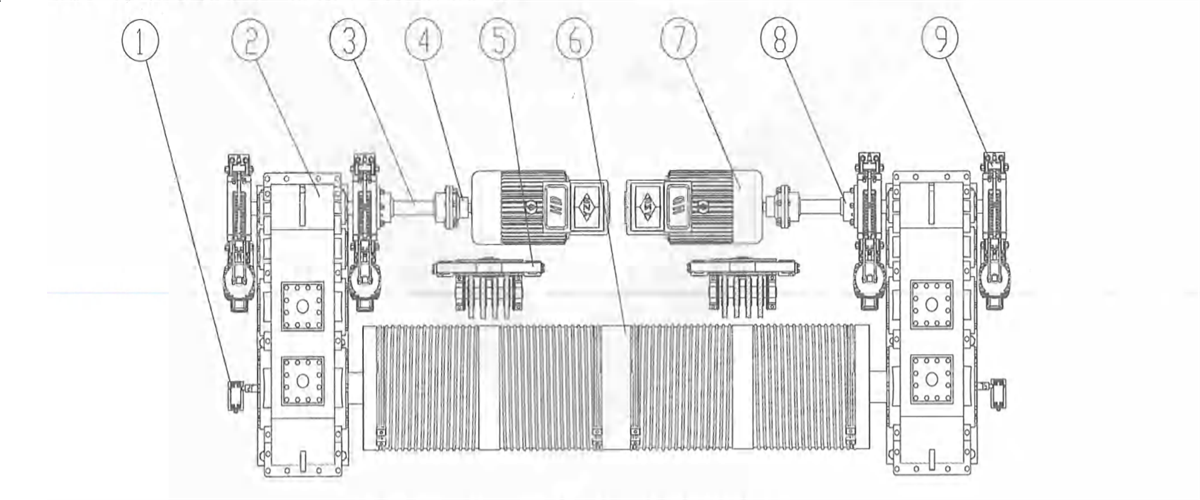
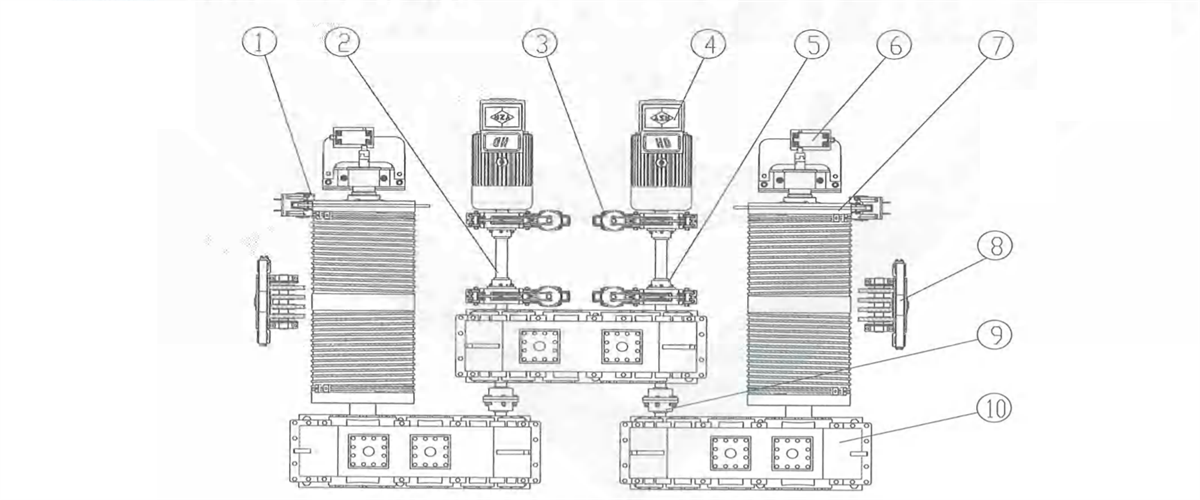
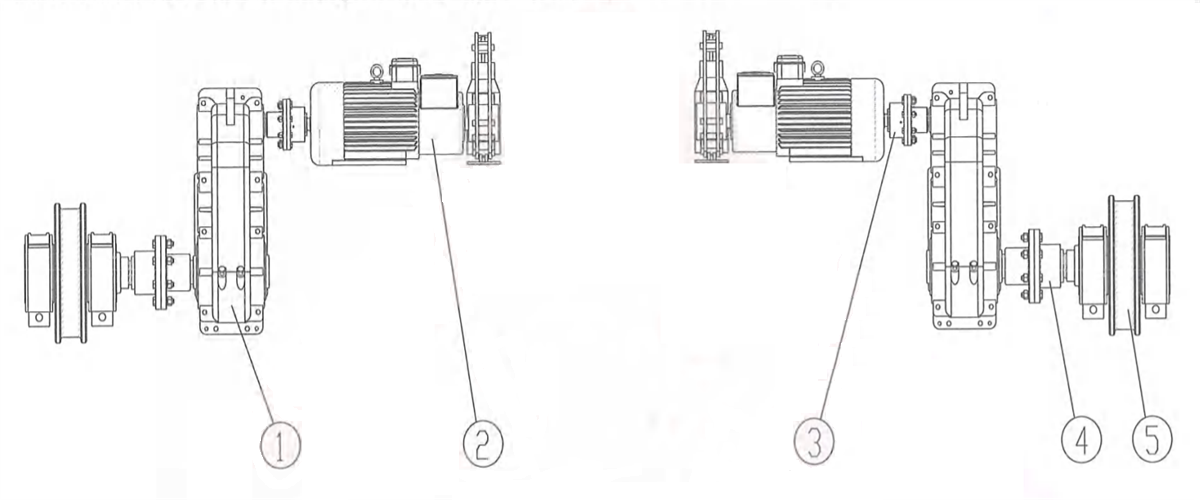
1) Centralized transmission: one motor fixed on trolley frame driving the vertical reducer to drive the wheels on both sides to rotate through two transmission shafts. it’s applicable to four-wheel medium and small tonnage rated lifting ladle crane’s trolley.
Figure 2-13 Vertical Centralized Transmission
1-brake 2-coupling 3-motor 4-vertical reducer 5-transmission shaft 6-wheel block
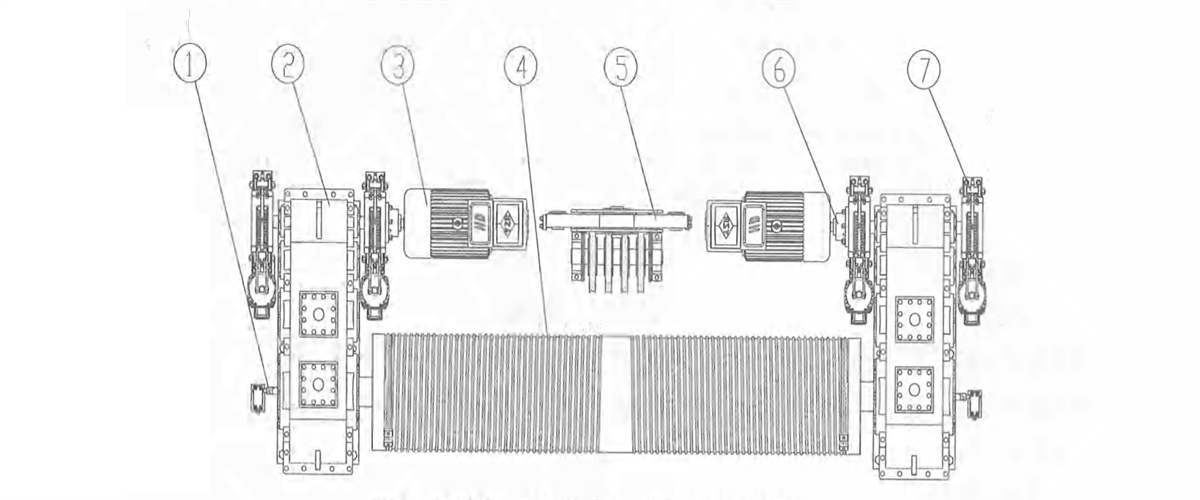
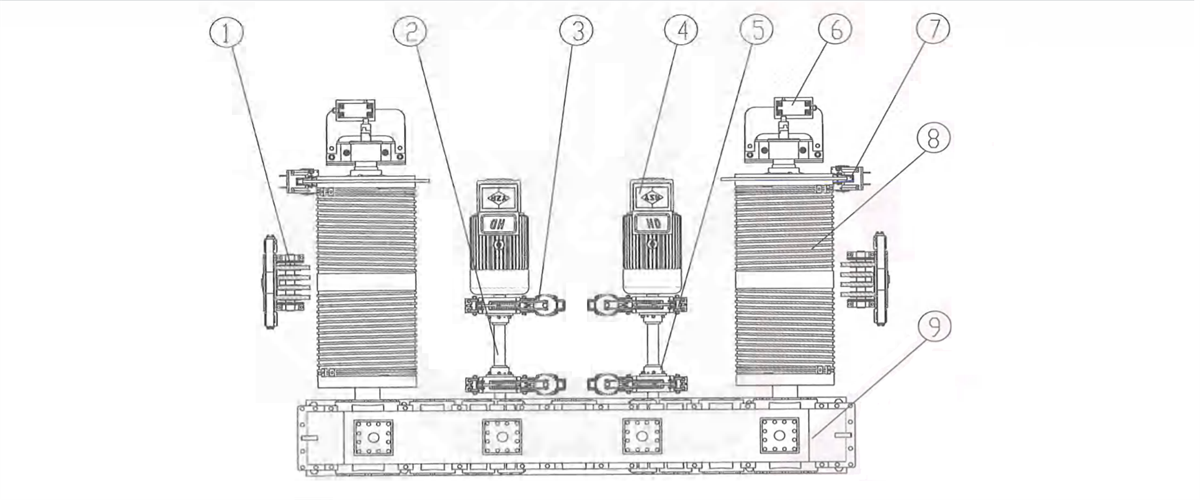
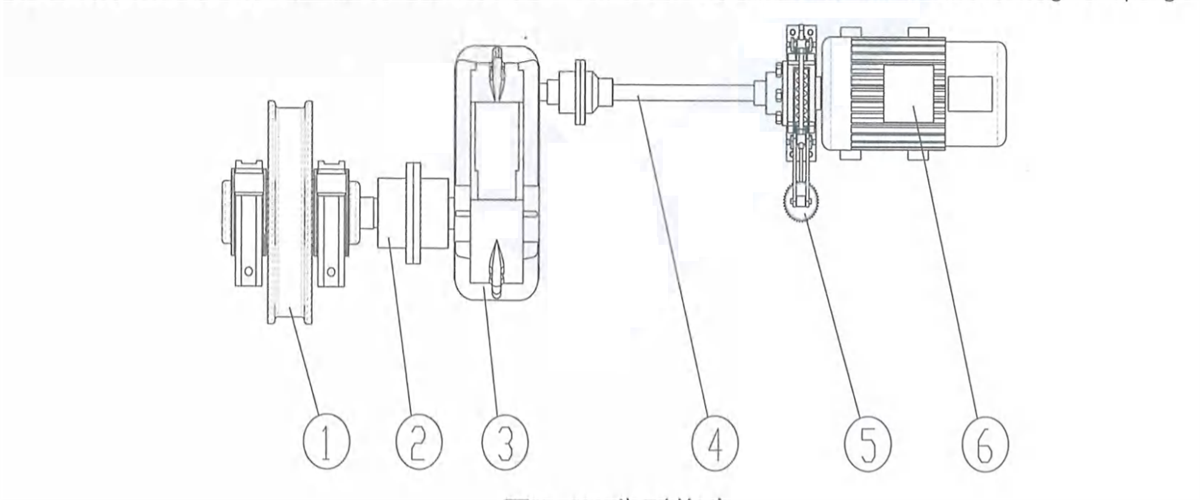
2) Respective transmission: two motors fixed on trolley frame will drive two vertical reducers respectively to drive the wheels on both sides to rotate through the coupling. It is applicable to four-wheel trolley.
Figure 2-14 Vertical Respective Transmission
1-verticalreducer 2-motor 3-coupling 4-coupling 5-wheel block
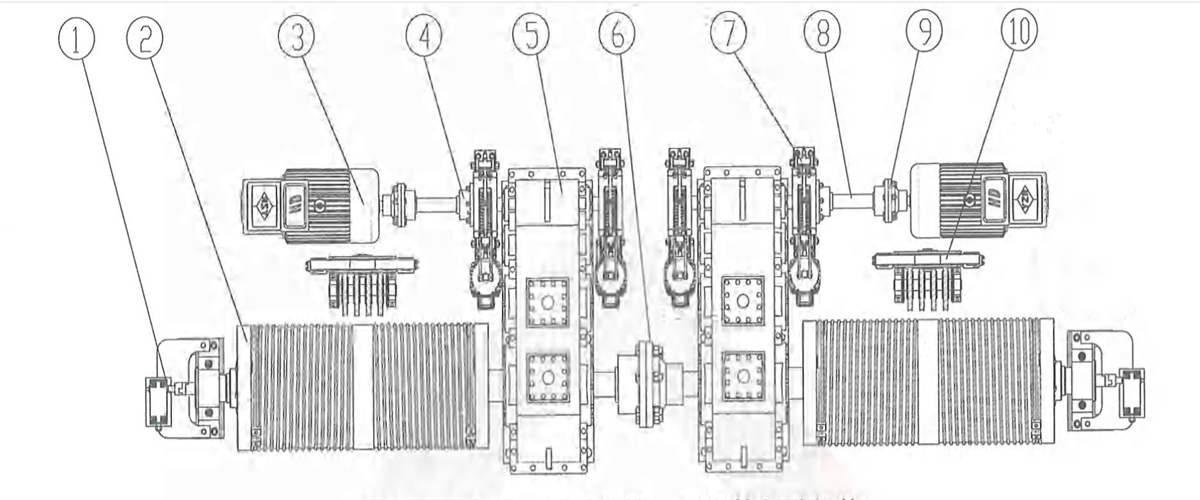
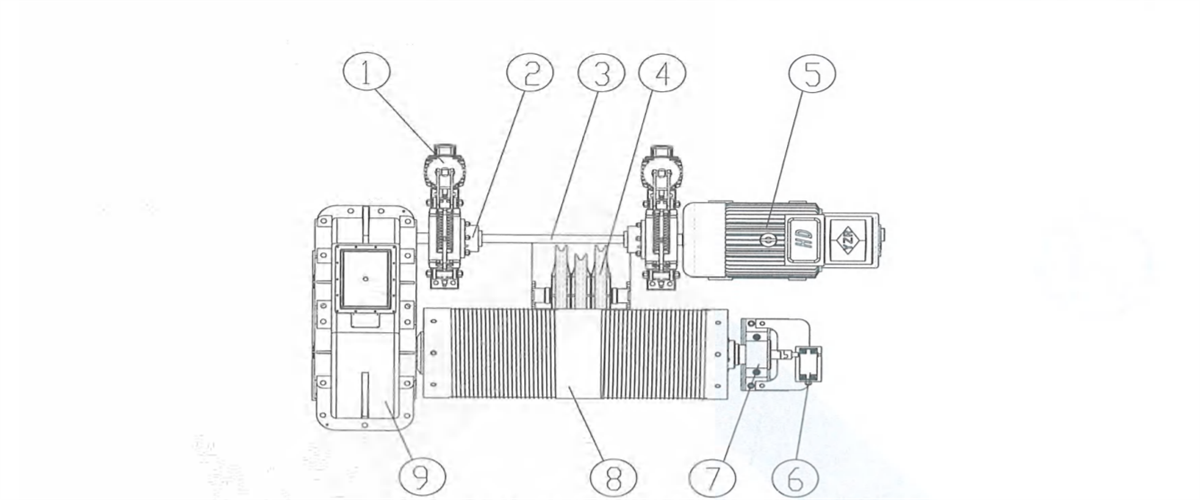
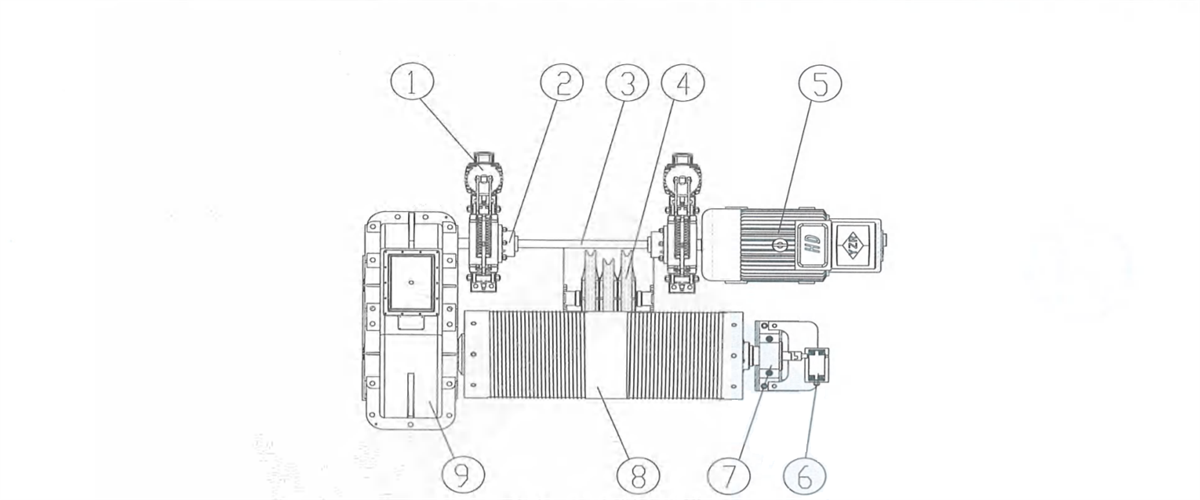
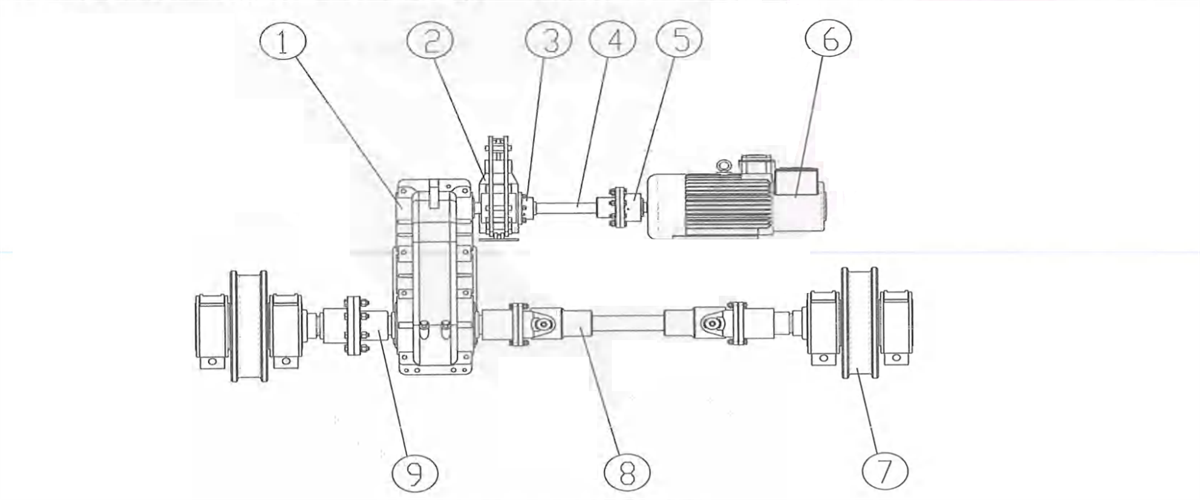
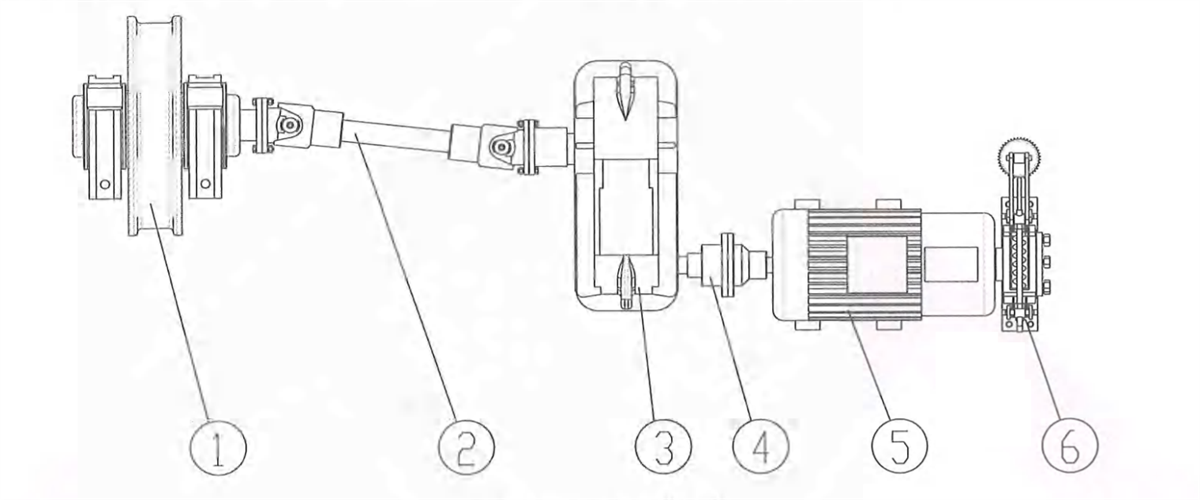
3) Respective transmission: two motors fixed on trolley frame, driving two vertical reducers respectively to drive the wheels on both sides to rotate. The reducer is mounted next to wheel side. One side will drive the wheel through coupling and one side will drive the wheel through universal coupling. t’s applicable to eight-wheel trolley with four girders and six rails.
Figure 2-15 Vertical Centralized Transmission
1-reducer 2-brake 3-brake wheel coupling 4-transmission shaft 5-coupling 6-motor 7-wheel block 8-universal coupling 9-coupling
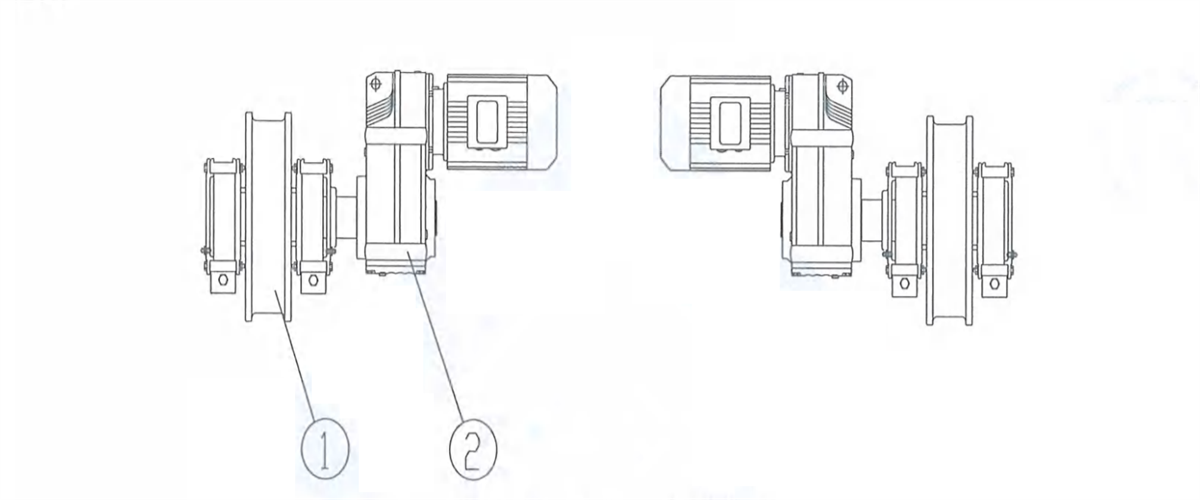
4) Three-in-one respective transmission: employ 2 three-in-one reducing motors to drive the wheels on both sides to rotate directly.
Figure 2-16 Three-in-one Respective Transmission 1-Wheel Block 2-three-in-one reducing motor
2.3 Crane long travelling mechanism
Kingda ladle crane(casting crane)long travelling mechanism consists of motor, reducer, brake, transmission shaft, coupling, wheel block, buffer, etc. and can drive the crane to move longitudinally along the rail. The long travelling mechanism has 2 transmission forms:
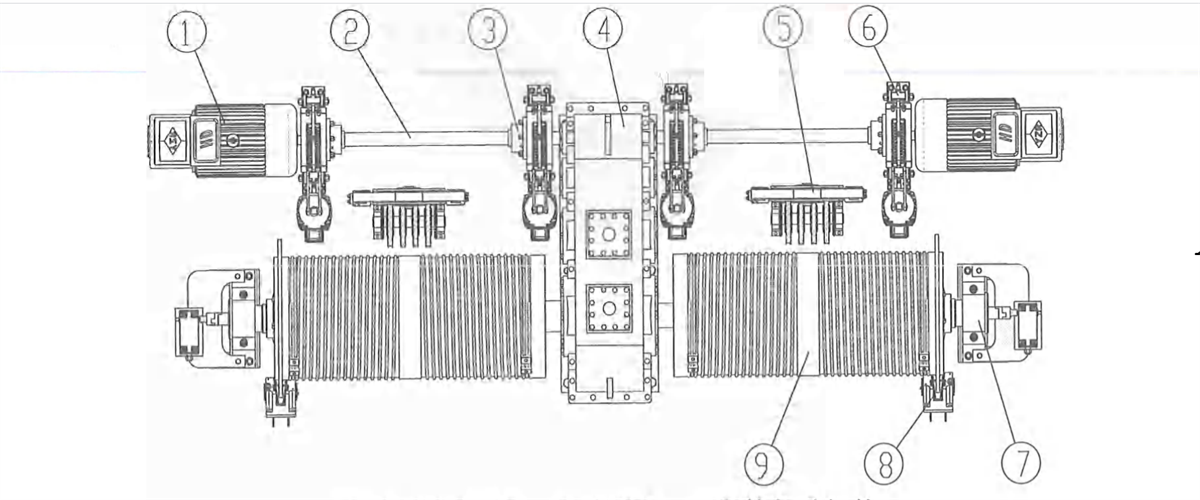
1) Respective transmission: two or four motors will deliver the power to the reducer through coupling and transmission shaft respectively, and low-speed shaft of the reducer will drive the wheels on both sides to rotate through coupling.
Figure 2-17 Respective Transmission
1-wheel block 2-coupling 3-reducer 4-transmission shaft 5-NC brake 6-motor
2) Respective transmission: 2 or 4 motors will drive the reducer respectively, so as to drive the wheels on both sides to rotate through universal coupling (or transmission shaft). The motor and reducer will be connected through coupling. while the reducer and wheel block shall be connected by universal coupling (or transmission shaft).
Figure 2-18 Respective Transmission
1-wheel block 2-universal coupling 3-reducer 4-coupling 5-motor 6-brake
2.4 Bridge frame
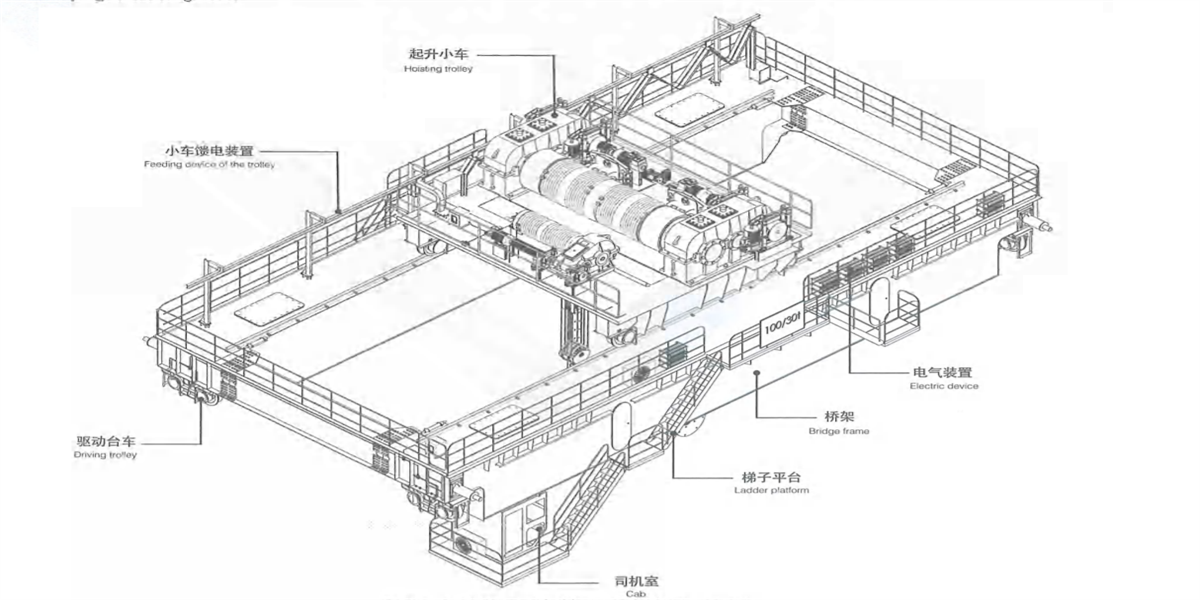
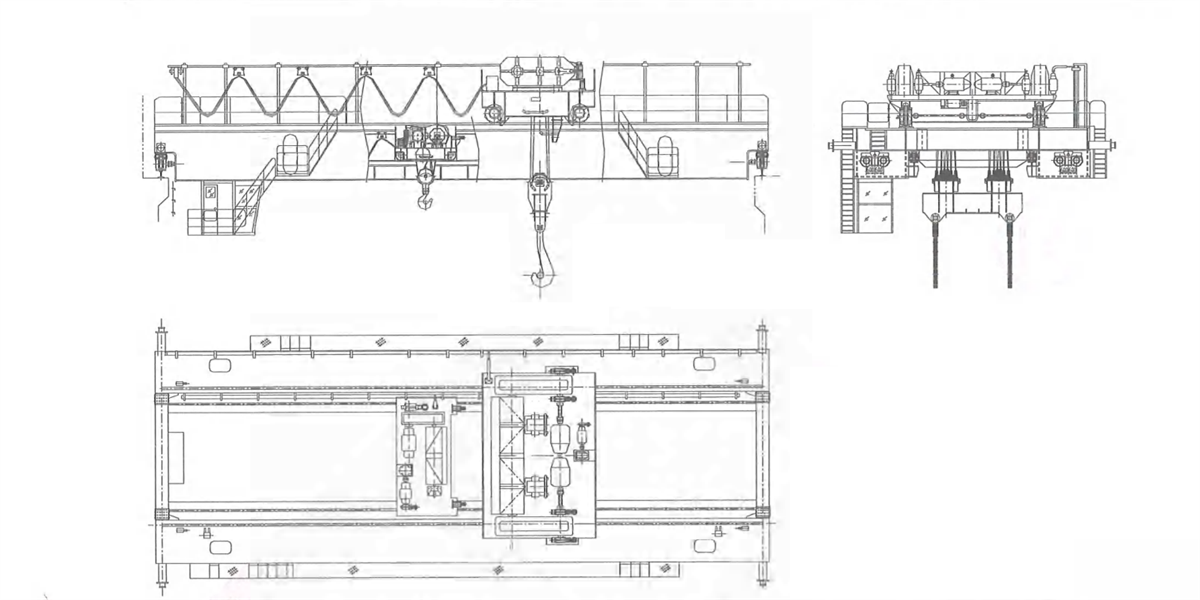
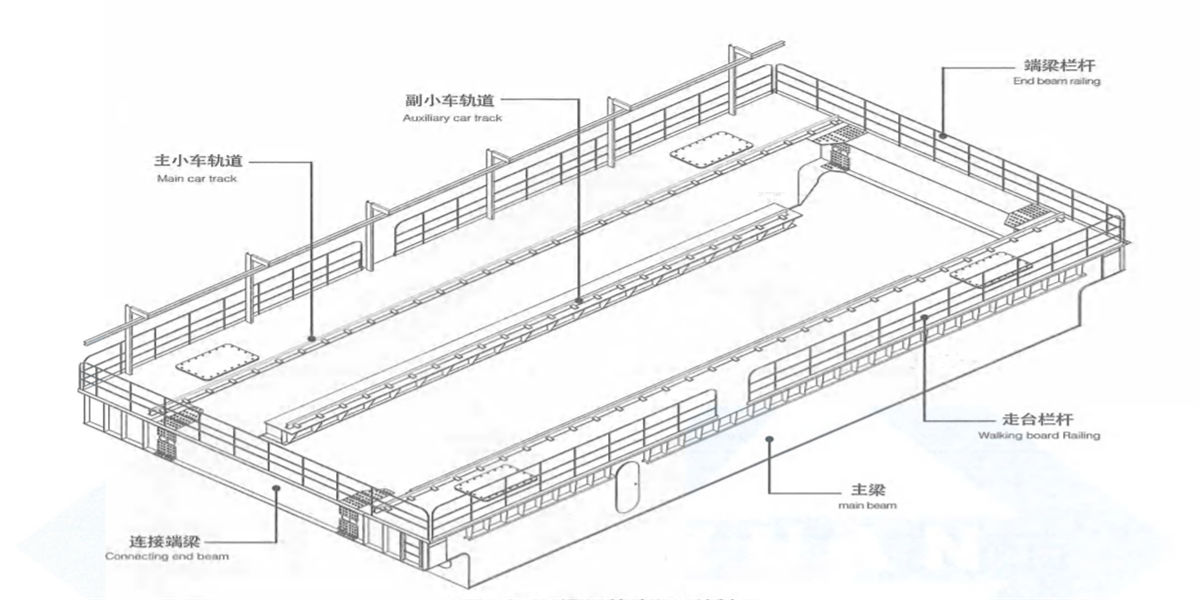
2.4.1 Kingda ladle crane (or casting crane) bridge frame is box-type double-beam or four-beam structure and consists of main beam, end beam, railing, walking board and accessories.
2.4.2 It is divided into three types according to different lifting capacity:
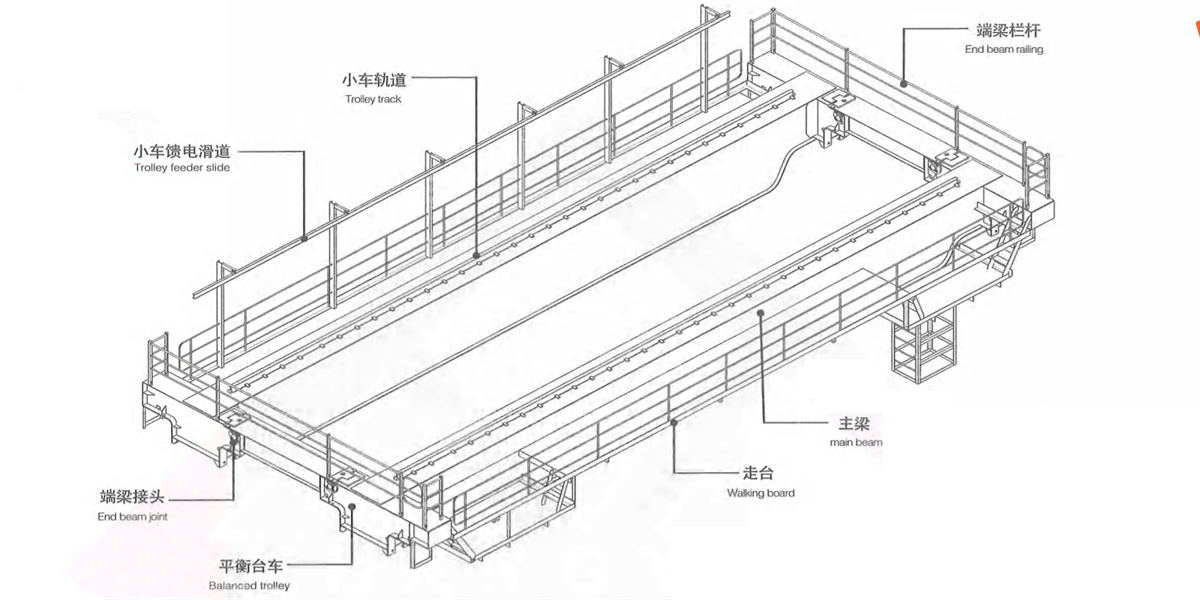
1) Double beam double rail - four wheels - narrow beam type bridge frame: middle rail or semi-off-rail or off-rail of trolley rail is arranged on the main beam (Figure 2-15a, b & c). Walking board is set on both sides of the main beam and consists of section steel and checkered plate. The walking board on transmission side is used to place crane long travelling mechanism and electric devices, the walking board on the driven side is used to place power feeding device-cable trolley. For convenient transportation, the main beam and end beam are welded as a whole, a joint is arranged in the middle of end beam to realize bolt connection for disassembling the bridge frame in two parts. This type casting crane is applicable small tonnage rated lifting capacity.
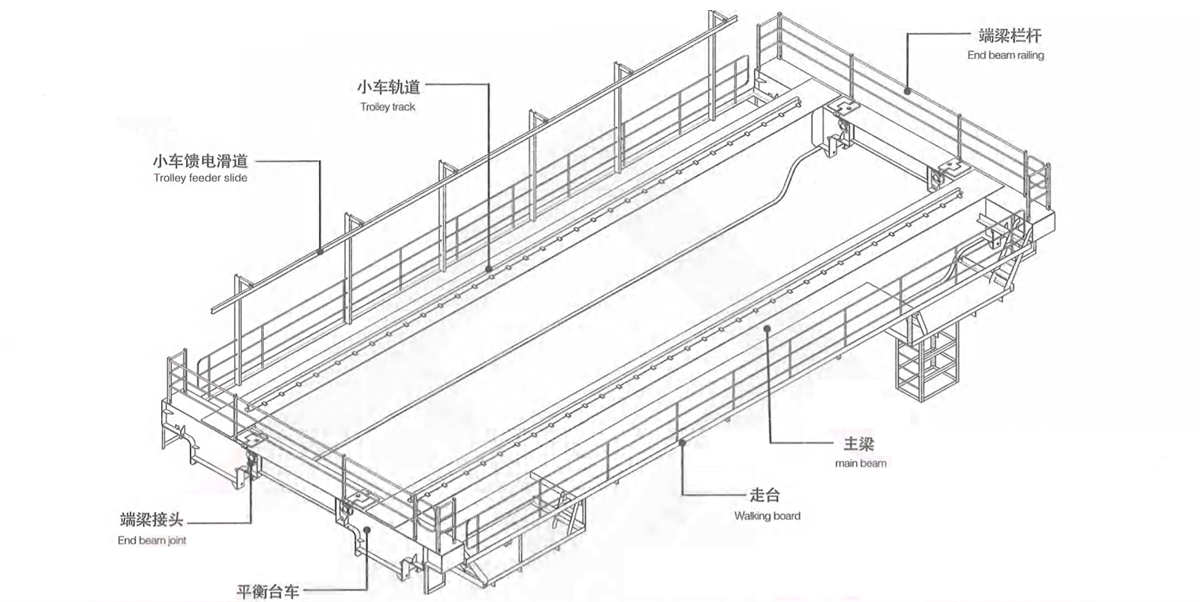
Figure 2-19 double beam double track four wheeled narrow beam type bridge frame
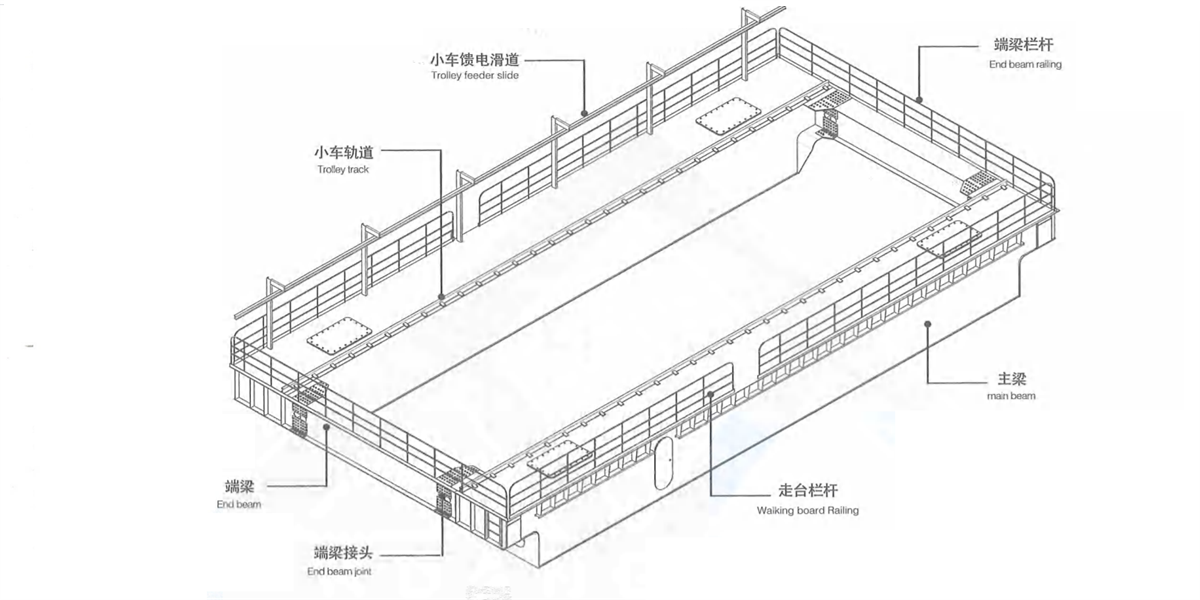
2) Double beam- Double rail- Eight wheels- narrow beam type bridge frame: middle trolley rail or semi-off-rail or of-trolley rail is arranged on the main beam (Figure 2-16a, b & c). Walking board is set on both sides of the main beam and consists of section steel and checkered plate. The walking board on transmission side is used to place crane long travelling mechanism and electric devices, while the walking board on the driven side is used to place power feeding cables trolley. The main beam and balancing bogies are welded into the whole, there is a connecting end beam between the bogies to realize bolt connection for disassembling the bridge frame into two parts for convenient transportation. This ladle crane is applicable to medium and small tonnage rated lifting capacity.
Figure 2-20 double beam double track eight wheeled narrow beam type bridge frame
3) Double beam-double rail-wide beam type bridge frame: the main beam is wide-flange box-type structure. The upper part can be used as the channel of walking board. Off-track of trolley rail is arranged (Figure 2-16d) on the main beam, crane long travelling mechanism and electric devices are arranged inside the main beam, and there is an access door for personnel access. The main beam and box-type end beam employ bolt or pin connection for disassembling the bridge frame into two parts for transportation convenient. This ladle crane form is applicable to the large tonnage rate lifting capacity.
Figure 2-21 Double beam double track wide beam type bridge frame
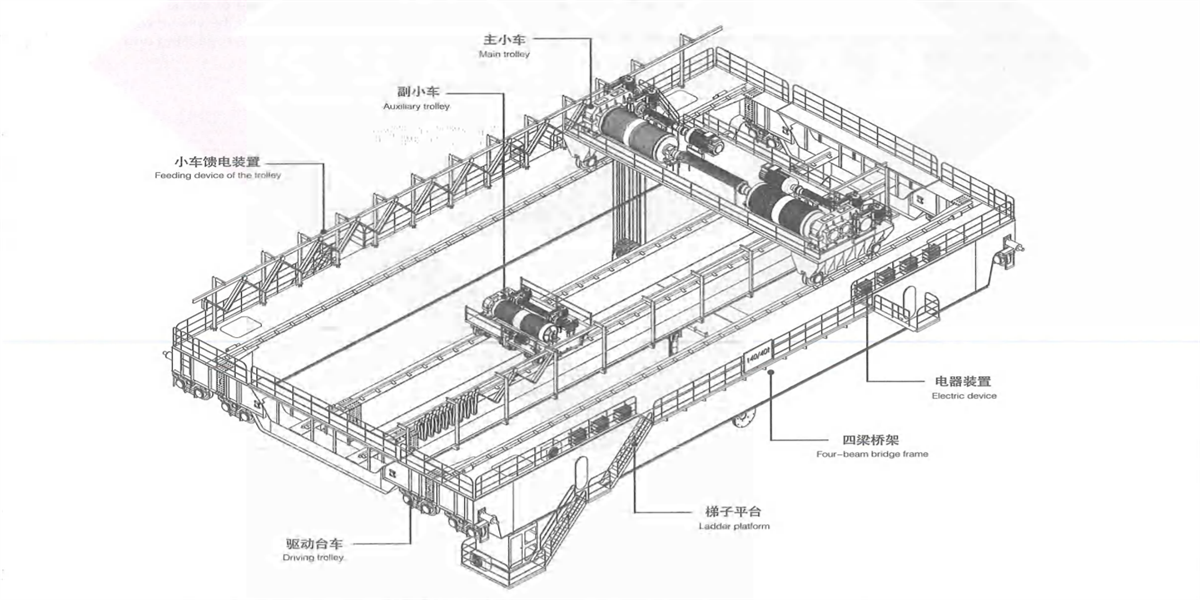
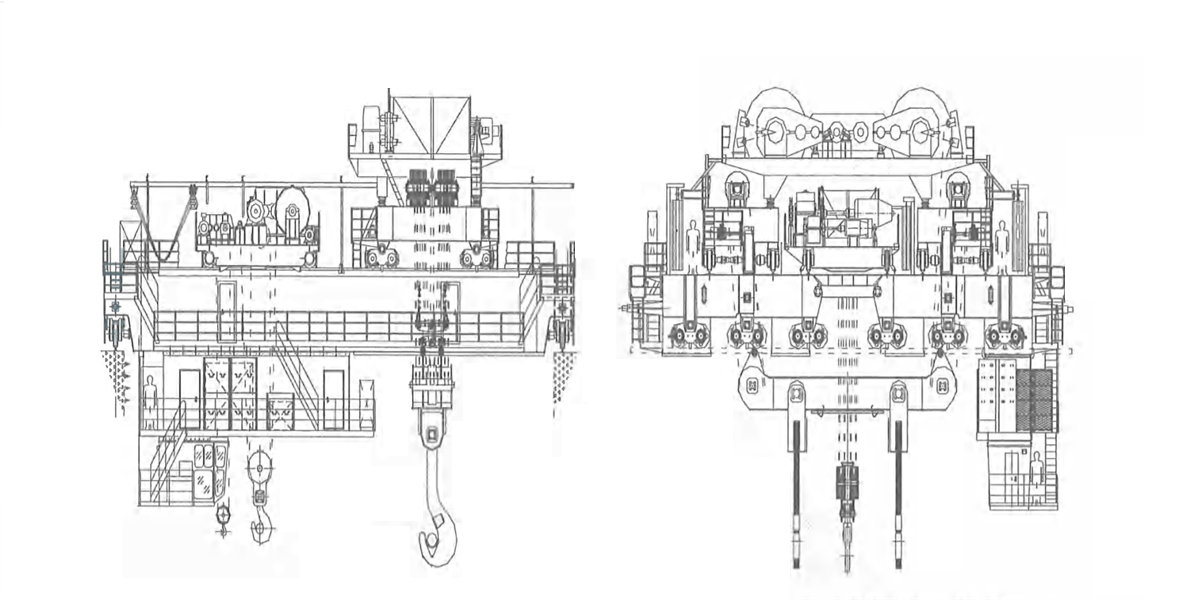
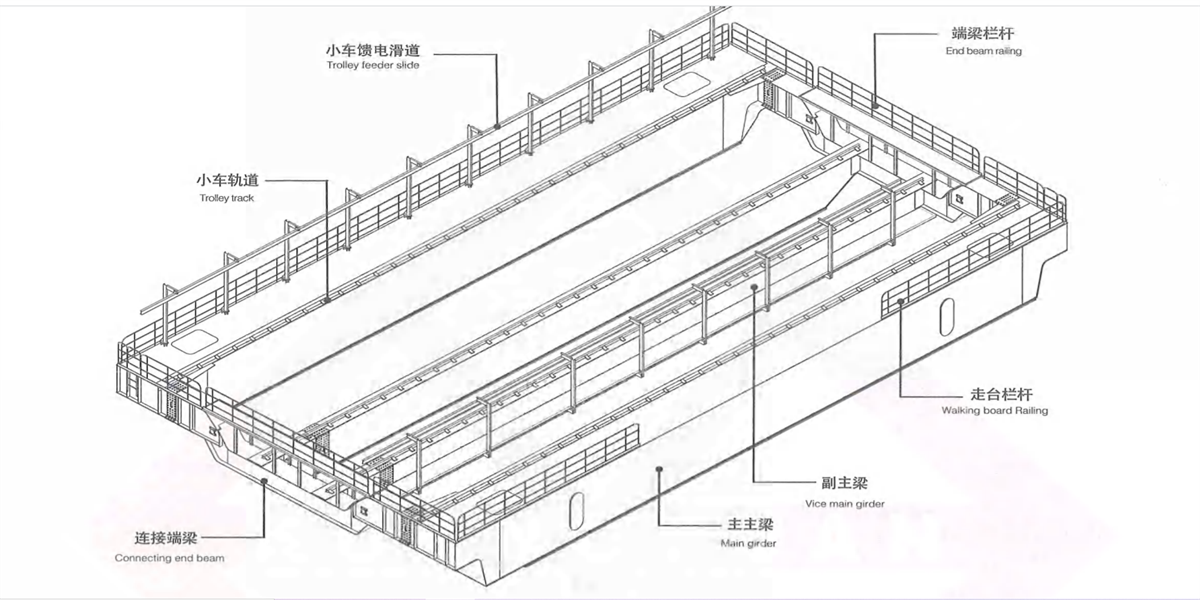
4) Four-beam & four-track wide beam type bridge frame: it consists of two main beams, two auxiliary main beams, two end beams and accessories. The main beam is wide flange box-type structure. Upper part can be used as the passage of walking board. The trolley rail is arranged on the main beam in off-track form (Figure 2-24d), crane operating mechanism and electric devices are arranged inside the main beam and access door is set for the access of relevant personnel. Auxiliary main beam is rich-track or off-track box-type narrow beam structure. One side is configured with walking board which is used to place cable trolley feeding device. The main beam and box-type end beam adopt bolt or pin connection, which is convenient for disassembling the bridge frame into two parts for transportation. This ladle crane is applicable to the medium and large tonnage rated lifting capacity.
Figure 2-22 Four-beam & Four-track Wide Beam Type Bridge Frame
5) Double-beam-four-rail wide beam type bridge frame: the main beam is wide flange box-type structure. Main and auxiliary trolleys share two main beams. The rail of main trolley is arranged on the main beam in off-track form, while the track of auxiliary trolley is arranged under inner side of the main beam (Figure 2-24e). Crane long travelling mechanism and electric devices are arranged inside the main beam, access door is set for the access of relevant personnel. The main beam and box-type end beam adopt bot or pin connection, which is convenient for disassembling the bridge frame into two parts for transportation. This ladle crane is applicable to medium and small tonnage rated lifting capacity.
Figure 2-23 Double-beam & Four-track Wide Beam Type Bridge
Figure 2-24 Main Beam Form
2.4.3 According to different structures, kingda ladle crane (or casting crane) end beam’s joint type falls into rigid type and flexible type.
1) Rigid angle steel type joint: the end beam‘s upper cover plate and web plate adopt angle steel type bolt connection. The lower cover plate adopts plate-type bolt connection. It is applicable to the ladle crane with medium and small tonnage rated lifting capacity. Please refer to Figure 2-25:
2) Rigid plate-type joint: the joint area adopts plate-type bolt connection. It is applicable to the ladle crane with large tonnage rated lifting crane. Please refer to Figure 2-26;
3) Flexible pin-type joint: the joint area adopts pin connection, lt is applicable to the ladle crane with large tonnage. Please refer to Figure 2-27 and Figure 2-28.

Figure 2-25 Rigid Angle steel Type Joint

Figure 2-26 Rigid Plate-type Joint

Figure 2-27 Flexible Pin-type Joint

Figure 2-28 Flexible Pin-type Joint
2.5 Main parts and components
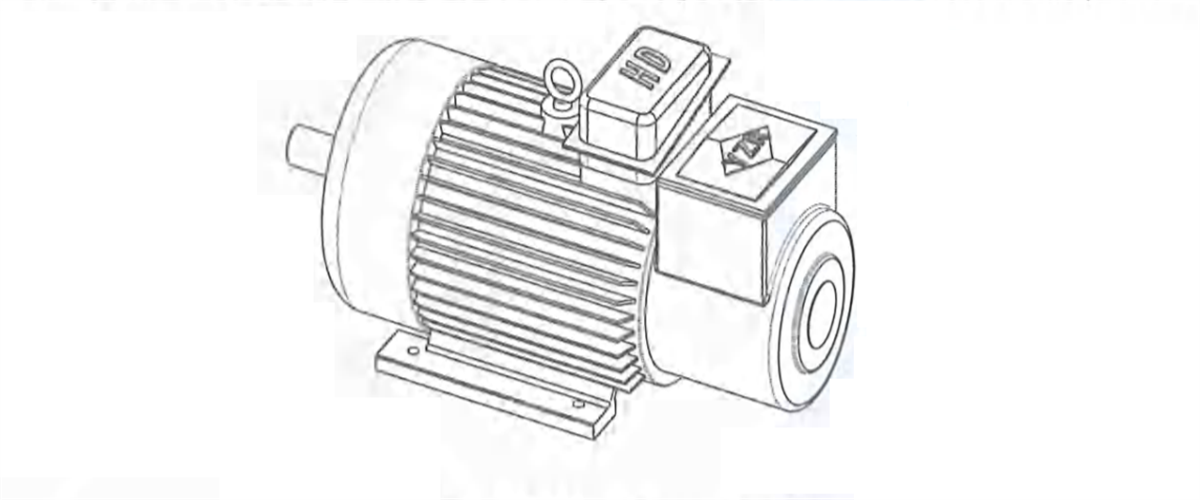
2.5.1 Motor
Kingda ladle crane (or casting crane) motor is YZR type three-phase asynchronous motor used for lifting and metallurgy industry, insulation grade: H, protection grade: IP54-65. It is applicable to short-term or intermittent period work. Lt is also able to employ frequency converter motor according to actual demand, which can cooperate with the frequency converter to realize 1:10 speed control.
Rated parameter values of the motor are confirmed on the basis that working environmental temperature is not higher than 40'C and the altitude doesn't exceed 1 000m. In case any environmental factor changes, it will influence motor characteristics, please consult the manufacturer for specific working condition.
Figure 2-29 Motor
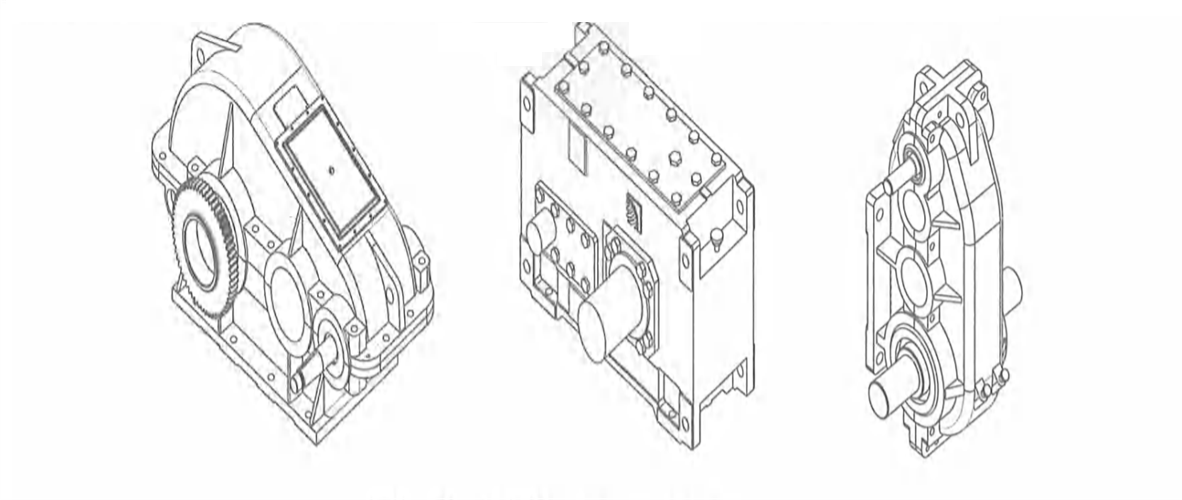
2.5.2 Reducer
Kingda ladle crane (or casting crane) reducer is a closed cylindrical gear transmission structure and an important transmission component for casting crane. It mainly plays the role of reducing high speed of the motor to working speed required by each mechanism. It can be mounted horizontally, vertically and by three pivot points. Horizontal installation is mainly used for hoisting mechanism and crane long travelling mechanism, while vertical installation is mainly used for trolley cross travelling mechanism. It can be divided into soft gear surface, medium-hard gear surface or hard gear surface according to the hardness of gear surface. The housing employs casting or welding structure and low-speed out shaft employs C-type gear plate or cylinder axis form
Figure 2-30 Reducer
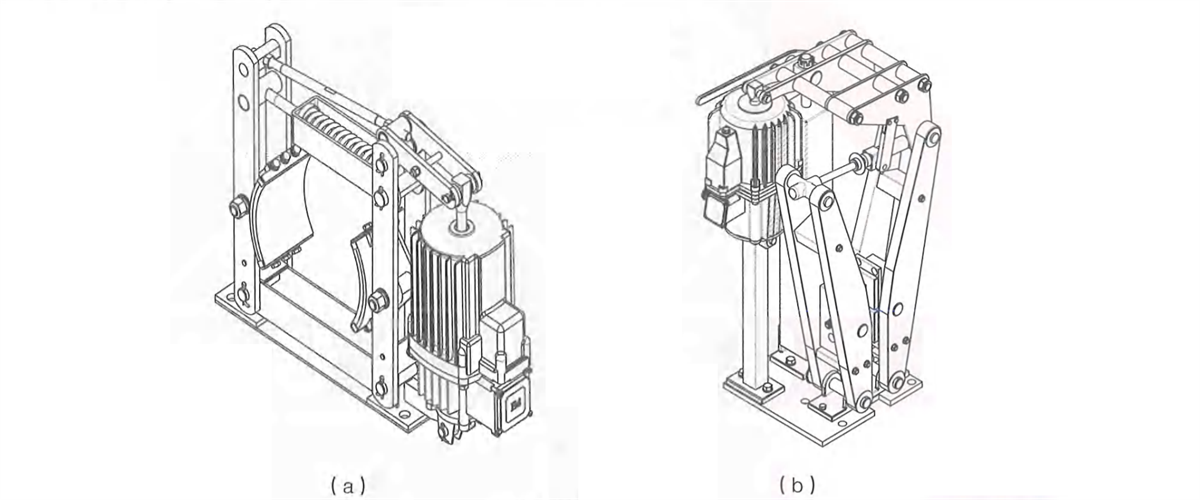
2.5.3 Brake
Kingda ladle crane (or casting crane) NC electric hydraulic brake will be opened during power-on and closed during power-of. t’s mounted on high-speed
shaft of the working mechanism to reduce braking torque.it can be attached with gasket abrasion automatic compensation, manual release, opening & closing limit and other special functions. lt can be divided into two structures according to structural form, namely, branch wheel type (Figure 2-31a) and plate type (Figure 2-31b).
Figure 2-31 Brake
2.5.4 Drum
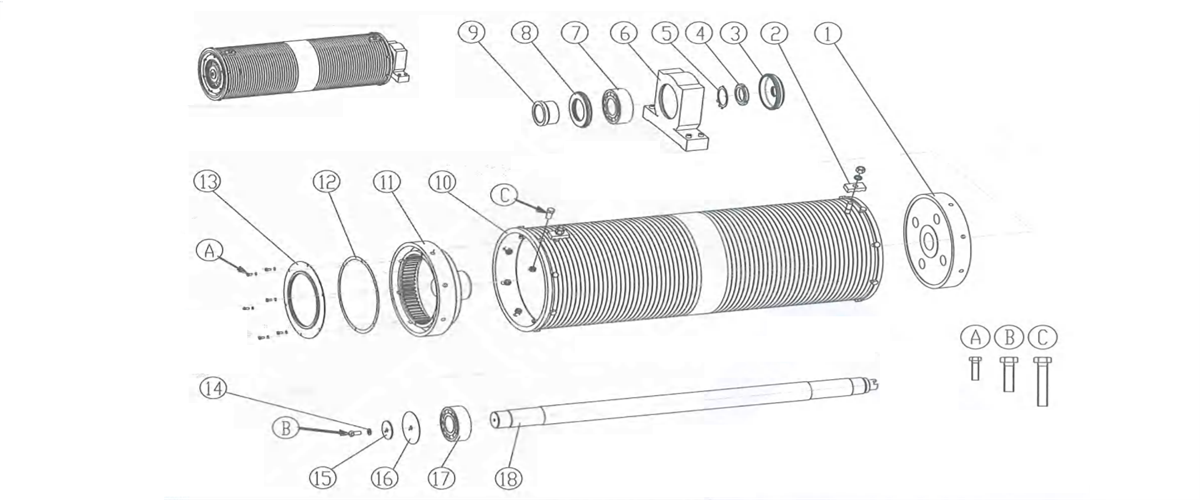
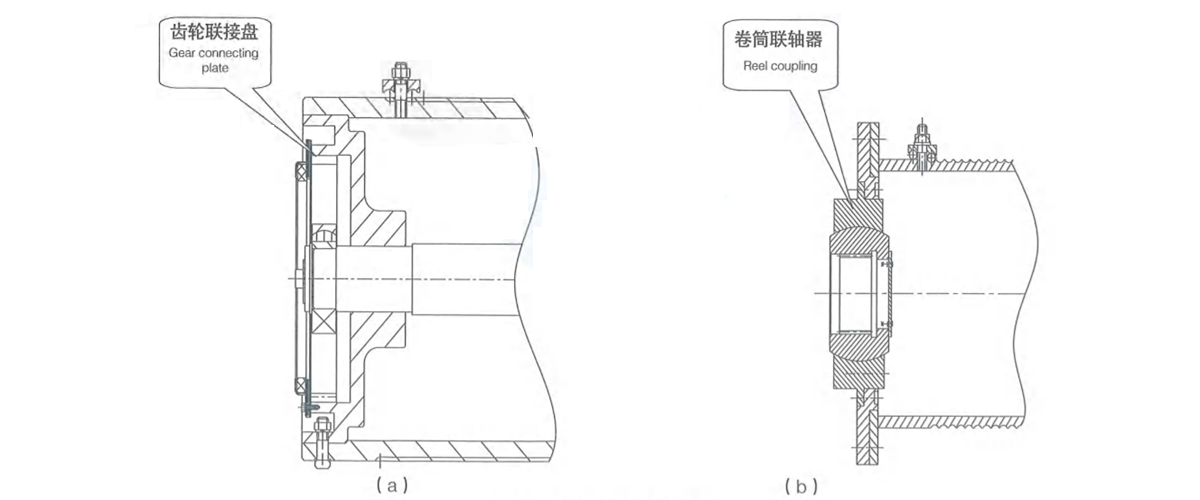
Kingda ladle crane (or casting crane) drum is the component in hoisting mechanism for winding steel rope, is made by steel plate through coiling, and employs long-axis or short-axis type tube structure. It adopts tooth-form connecting plate (Figure 2-33a) or reel coupling (Figure2-33b), etc. to connect with reducer coupling end. The other end is configured with bearing pedestal for fixing and supporting and overload limiter, rotary limit switch and other accessories can be mounted on shaft end.
The drum surface is machined with spiral rope groove, steel rope will wind it in a single layer, and pressing plate for fixing steel rope is mounted.
Figure 2-32 Long axis Reel Block
1-reel hub 2- pressing plate device 3-holed cover -round nut 5- washer 6-overload limiter 7-bearing8-holed cover
9-spacer bush 10-reel 11-gear plate coupling 12-pad 13-eparable cover 14-stop pad 15-cover plate 16-base plate 17-bearing 18-shaft A/B/C-fastening bolt
Figure 2-33 Connecting End of Drum Block
2.5.5 Pulley block
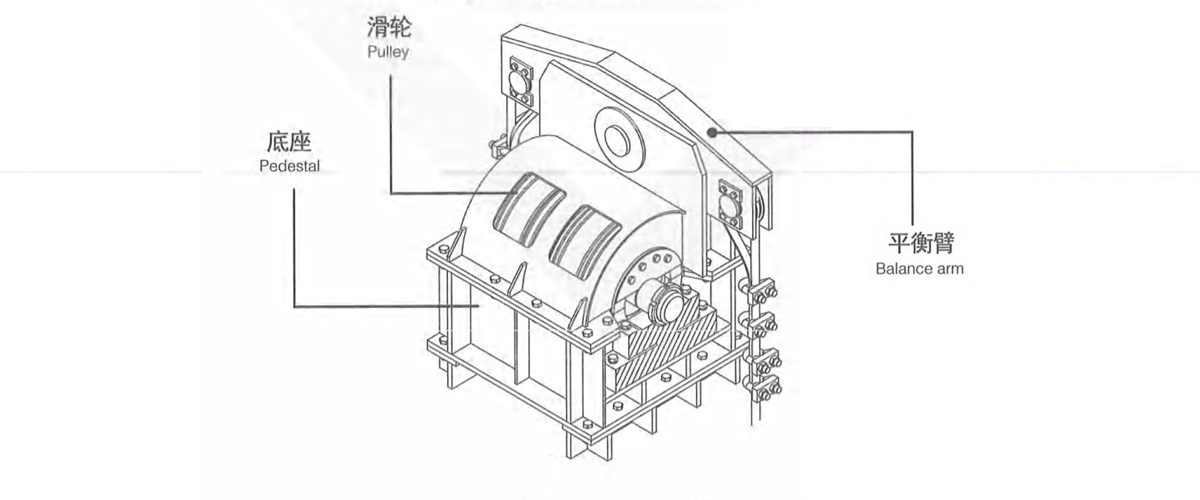
Kingda ladle crane (or casting crane) pulley block is used to guide the direction of steel rope and balance the branch tension of steel rope. lt can be divided into cast steel pulley or steel plate rolled pulley according to different materials. The main hoisting pulley block adopts balance arm structure.
Figure 2-34 Pulley Block of Aux. Pulley Block
1-fastening bolt 2-crane body 3-base plate 4-shaft end baffle 5-washer 6-nut 7-shaft 8-pulley 9-spacer bush 10-washer 11-round nut
Figure 2-35 Pulley Block of Main Hoisting Pulley Block
2.5.6 Spreader
2.5.6.1 Hook block.
Kingda ladle crane (or casting crane) hook block is the picking up device used most commonly on the crane, and consists of the hook with straight shank, hook nut, thrust bearing, hook cross beam, pulley, pulley shaft, pulling plate, etc. Shank part of the hook is machined with screw thread for mounting the nut to fix the hook. Thrust bearing is mounted inside the cross beam, which can make the hook rotate flexibly, to prevent the unhooking of steel rope, safety jaw is set in hook mouth to play the role of preventing unhooking.
The hook with straight shank is mainly forged by Q345B bridge steel.
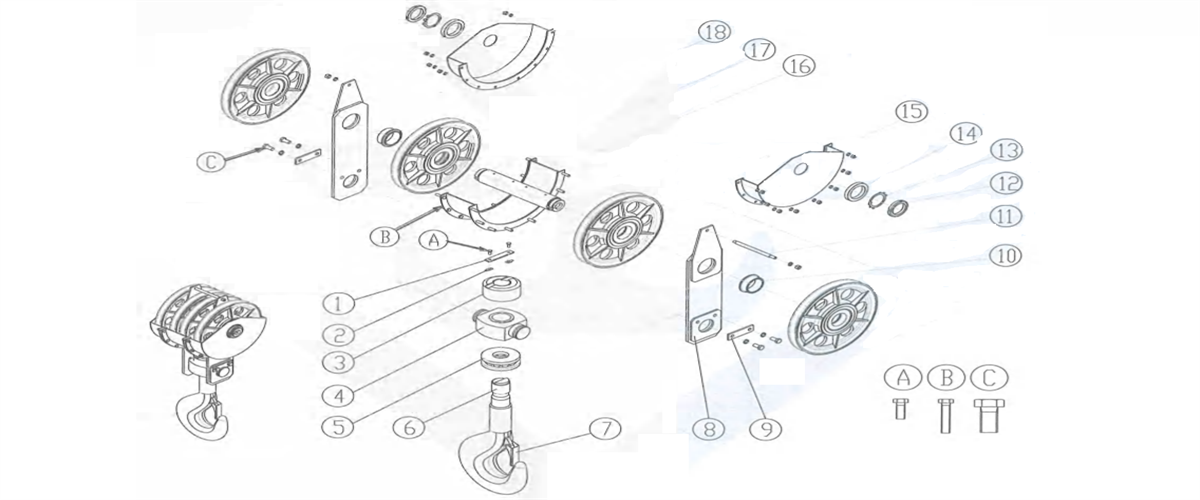
Figure 2-36 Hook Block
1-locating plate 2-stop washer 3-base plate 4-hook nut 5-bearing
6-hook 7-safety jaw 8-voke plate 9-end shaft baffle 10-spacer bush 11-stud 12-round nut 13-washer 14-spacer bush
15-outer cover of the pulley 16-middle cover of the pulley 17-shaft 18-pulley A/B/C-fastening bolt
2.5.6.2 Gantry-type laminated plate hook
Kingda ladle crane (or casting crane) Gantry-type laminated plate hook is used to convey the vessel with molten metal and consists of movable pulley block suspended beam, plate hook, thermal insulating device, etc. The lifting steel rope is wound on movable pulley group, the suspended beam is box-type structure, the plate hook is made by multiple hook pieces cut along the rolling direction through riveting and there is wearproof liner at the mouth of hook. According to different lifting weight and functions, there are many forms:
Form l: the suspended beam is configured with movable pulley block, the distance between shank hooks is fixed and the tail end of steel rope is fixed on the balance arm of movable pulley block. Please refer to Figure 2-37.
Form Il: the suspended beam is configured with movable pulley block. The distance between shank hooks is variable and the tail end of stee rope is fixed on the balance arm of movable pulley block. Please refer to Figure 2-38.
Form Ill: the suspended beam is configured with movable pulley group, the distance between shank hooks is fixed and the tail end of steel rope is fixed on the balance arm of movable pulley group. Please refer to Figure 2-39
Form lV: it adopts rotational structure. It consists of movable pulley block, fixed suspended beam, slewing suspended beam slewing mechanism, thermal insulating device, shank hook, etc. The slewing mechanism is set on the fixed suspended beam. During the working, the slewing mechanism will drive the slewing suspended beam to rotate for 90’or 180’. Please refer to Figure 2-40.

Figure 2-37 Gantry-type Plate Hook with Fixed Distance
1-plate hook 2-movable pulley block 3-suspended beam 4-thermal insulating device

Figure 2-38 Gantry-type shrank Hook with Variable Distance
1-plate hook 2- suspended beam 3- thermal insulating device 4- movable pulley block
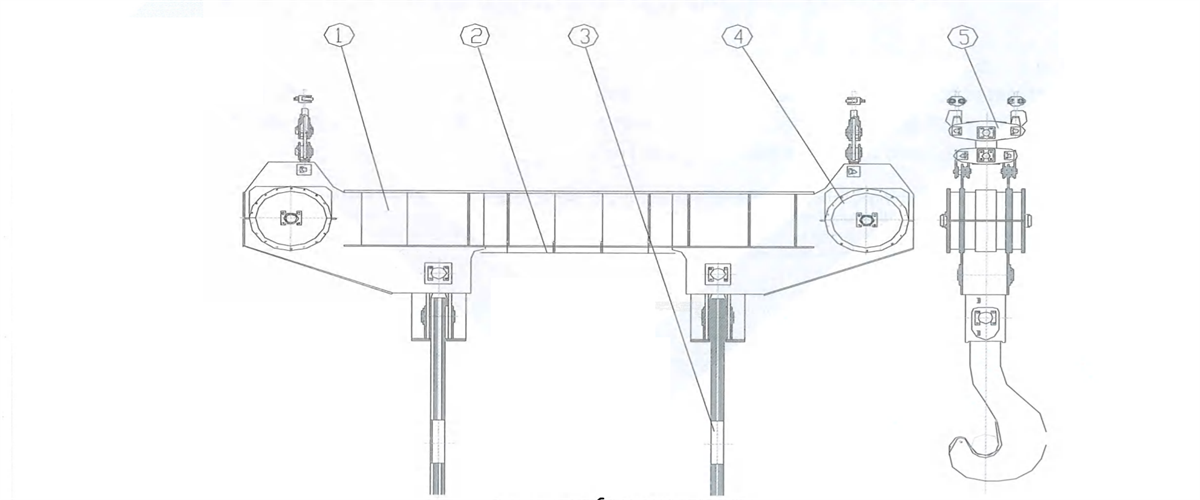
Figure 2-39 Gantry-type Shrank Hook with Fixed Distance
1-suspended beam 2-thermal insulating device 3-plate hook 4-movable pulley block 5-balance arm
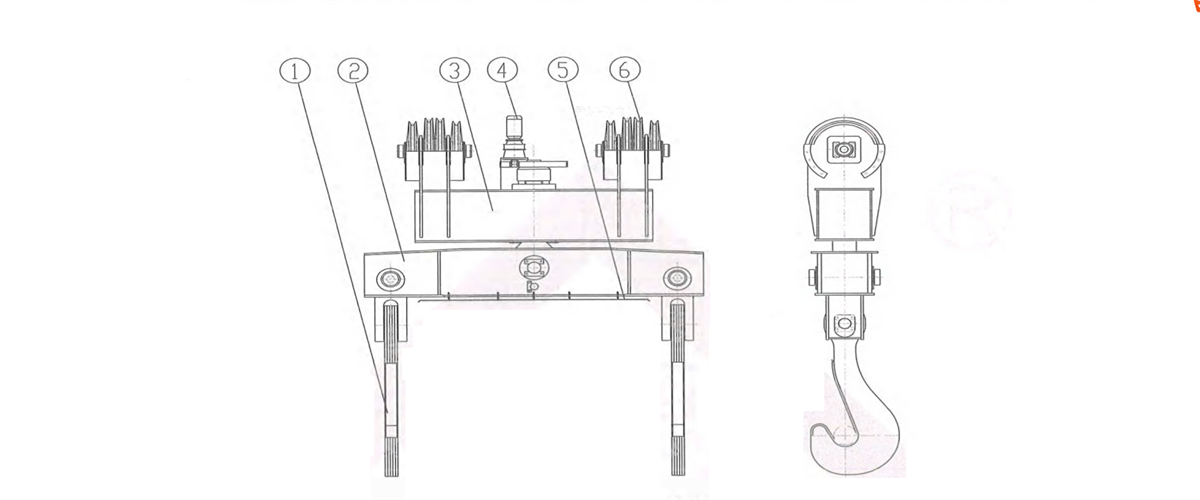
Figure 2-40 Rotational Gantry-type Shrank Hook
1-plate hook 2-rotational suspended beam 3-fixed suspended beam 4-driving mechanism5-thermal insulating device 6-movalbe pulley block
2.5.7 Coupling
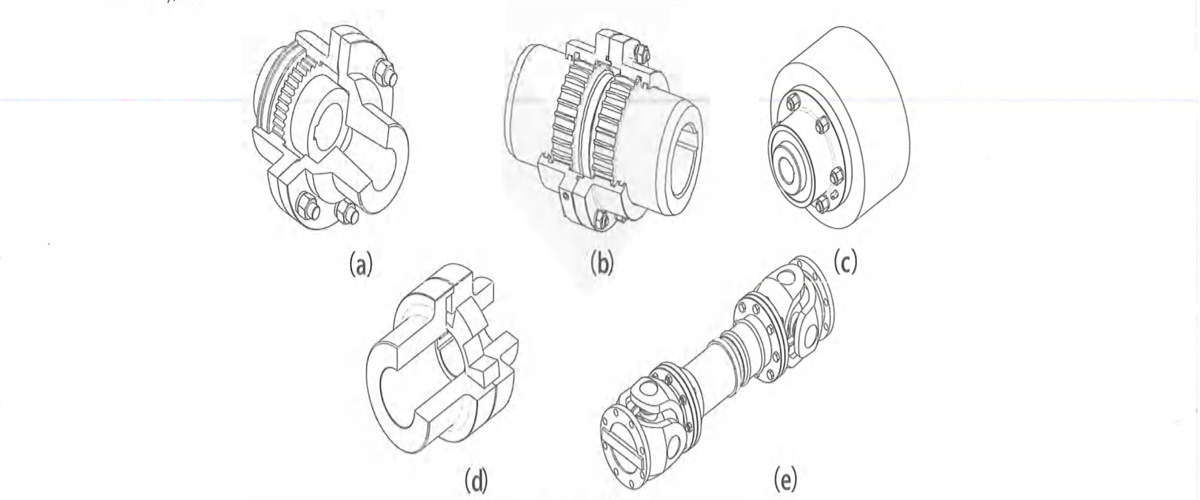
Kingda ladle crane (or casting crane) coupling is mainly used to connect two rotation shafts arranged in coaxial line to deliver torque and compensates light angular and radial deflection. The coupling commonly used by the crane includes straight-tooth coupling (Figure2-41a), crowned-tooth coupling (Figure 2-41b), brake wheel coupling (Figure 2-41c), coupling with elastic spider (Figure2-41d), universal coupling (Figure 2-41e), etc.
Figure 2-41 Coupling
Tooth coupling consists of internal tooth ring of the same number of teeth, flanged half-coupling with outer teeth, etc. Internal &external tooth rings and shaft coupling or brake wheel can also comprise semi-tooth coupling. According to different tooth shapes, outer tooth can be divided into straight tooth and crowned tooth. Outer tooth of crowned tooth coupling is aspherical surface, and the center of the surface is on tooth axis. The backlash in circular tooth is larger than general tooth. The crowned tooth coupling can allow relatively large angular displacement (relative to straight-tooth coupling), and can improve contact conditions of the tooth, improve the capacity of delivering the torque and prolong the service life. During the work. Two shafts of the tooth coupling will generate relative displacement. tooth surface of inner and outer teeth will carry out axial relative sliding periodically, which will certainly result in abrasion of tooth surface and power loss, Therefore, the tooth coupling shall
Work in good lubrication and sealing condition. Coupling with elastic spider consists of two identical half-couplings of protruded claw form and elastic components. It can realize the connection of two half-couplings by virtue of protruded claw support of quincunx elastic component placed on two half-couplings. t’s featured by compensation of relative deflection of two shafts, vibration attenuation and buffering. lubrication-free, etc. When replacing the elastic component, two half-couplings shall move axially. Elastic components can be made by polyurethane or cast nylon.
Universal coupling is mainly used for low-speed shaft transmission and has relatively large angular compensation ability by virtue of the features of its mechanism. the connected two shafts can realize continuous rotation in the condition that the two shafts are not on the same axial line and there exists axial included angle, and deliver the torque and move reliably. The included angles of two axes of the universal couplings in different structure styles are different, generally between 5’-15°
2.5.8 Wheel block
Kingda ladle crane (or casting crane) Wheel block is an important component of operating mechanism and consists of wheel, shaft, bearing box, etc. According to the structural style, it can be divided into angular bearing box (Figure 2-42) and 45’split bearing box
(Figure2-43). The wheels are double flanges.
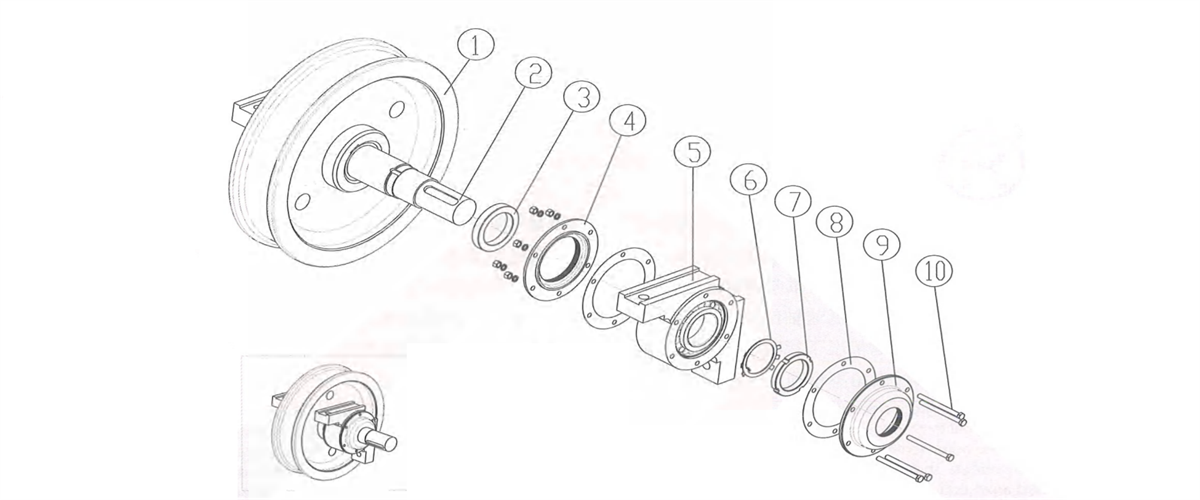
Figure 2-42 Angular Bearing Box Wheel Block
1-wheel 2-shaft 3-spacer 4-holed cover bush 5-angular bearing box 6-washer 7-round nut 8-adjustable pad 9-holed cover 10-fastening bolt
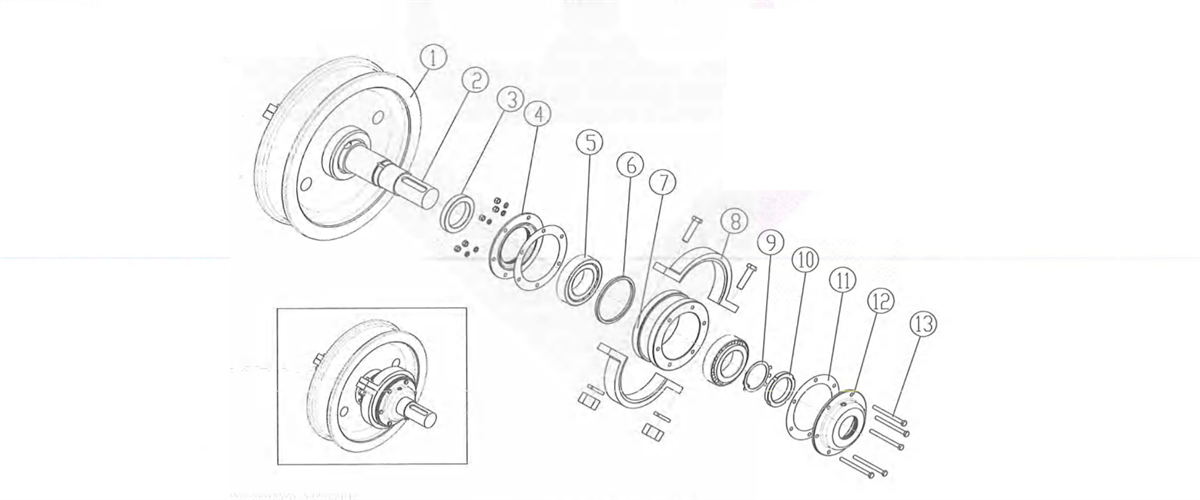
Figure 2-43 45° Split Wheel Block
1-wheel 2-shaft 3-spacer bush4-holed cover 5-bearing 6-spacer bush 7-bearing chamber8-housing of bearing chamber
9-washer 10-round nut 11-adjustable pad 12-holed cover 13-fastening bolt
2.6 Technical characteristics
Please refer to the drawing provided with the equipment for main technical parameters and overall dimension in detail